Projects
Speech Emotion Recognition Model
in progress
This project developed a machine learning system for speech emotion recognition (SER). SER is challenging due to the subjective nature of emotions, speaker variability, and real-world noise. The project aimed to design and implement a deep learning pipeline to process speech and predict emotional categories, enhancing audio-based machine learning. A core challenge is interpreting emotions from speech, a continuous signal with variable length, pitch, and style. Overlapping emotional expressions further complicate classification. This project explores deep learning models for extracting meaningful representations for emotion classification. The objective was to build a supervised learning model that takes audio files as input and predicts emotion labels, focusing on model development, training, and evaluation. The dataset comprised labeled speech audio files in a structured format, with folders for each emotion class. Key challenges included audio duration differences, noise, speaker variability, and class imbalance. The project was implemented in Python using PyTorch, Librosa for audio processing, NumPy for numerical operations, and Torchvision for leveraging pretrained CNNs. Scikit-learn was used for dataset splitting and evaluation. The system follows a pipeline: audio files are preprocessed, converted into tensors, passed through a neural network, and mapped to emotion predictions. Preprocessing involved normalizing the signal and padding/truncating to ensure consistent input length. A CNN based on a pretrained VGG16 model was used, leveraging transfer learning. The model was trained using cross-entropy loss and gradient-based optimization. Design decisions involved trade-offs between CNNs for feature extraction versus modeling temporal dependencies, fixed audio length for training feasibility versus potential information loss, and pretrained VGG for improved learning versus increased cost. Model performance was evaluated on a test set using accuracy and error analysis, revealing confusion between similar emotions. Challenges included handling noisy data, tuning parameters, and managing overfitting. The project demonstrated the subjective nature of emotion recognition. The codebase was modular, separating data handling, model definition, and training logic. A custom dataset class was implemented, and the training pipeline was designed to be extensible. Ethical considerations were addressed, acknowledging privacy risks and treating the model as a research exercise. Key learnings included understanding audio preprocessing, the advantages of transfer learning, and the limitations of CNNs for sequential data. Future improvements include transformer-based models, spectrogram representations, data augmentation, cross-dataset generalization, and continuous emotion dimensions, as well as multimodal emotion recognition. Overall, this project demonstrates skills in machine learning, deep learning, audio processing, and software engineering, showcasing the ability to work with complex data, reason about trade-offs, and evaluate model performance. The techniques are relevant to roles in AI, data science, machine learning engineering, and research.

LLM Based Search Engine
in progress
This project delivers relevant current affairs and auto-generated quizzes using large language models (LLMs), semantic embeddings, and news data. It retrieves, filters, and ranks news articles based on a user's topic, recommends related content, and generates factual quiz questions to enhance understanding.
Addressing the challenge of navigating vast real-time news, this project combines information retrieval with semantic filtering and LLM-based content generation to ensure relevance, coherence, and engagement. It aims to retrieve relevant articles, reduce noise, surface diverse perspectives, and transform passive reading into active learning.
The primary objective was to design a modular pipeline demonstrating skills in NLP, semantic similarity, system design, and LLM integration. This functional prototype emphasizes data flow, transparency, and extensibility.
The application captures user queries via CLI, web form, or API, applying input validation for robustness. It collects data using news APIs or RSS feeds, storing articles with metadata.
The filtering and ranking module uses semantic embeddings to rank articles by relevance, retaining only the top-N articles. A recommendation engine then suggests related content, promoting broader understanding.
The quiz generation module summarizes content and uses an LLM to generate multiple-choice, true/false, or short-answer questions, structured in JSON to test factual understanding.
The system follows a linear pipeline: query ingestion, data collection, semantic filtering, recommendation, and content generation. Modules are decoupled for independent testing and enhancement.
Technical trade-offs include balancing relevance with computational cost, limiting results to improve quality, and validating LLM-generated quizzes. These reflect real-world engineering considerations.
Challenges included handling varied article structures and ensuring semantic similarity aligns with user intent. Ensuring factual correctness in LLM-generated questions also proved difficult.
Key learnings include practical experience with semantic search, LLM integration, and modular system design. The project reinforces the distinction between information retrieval and understanding.
Future improvements include adding source diversity constraints, implementing confidence scoring for quizzes, supporting multilingual content, caching embeddings, and deploying the system as a web application. Additional extensions could involve difficulty-adjusted quizzes and longitudinal knowledge tracking.
Overall, this project demonstrates competence in NLP, semantic similarity, LLM integration, and system design. It showcases the ability to manage trade-offs and build learning-oriented applications using modern AI techniques, relevant to roles in data science, applied AI, machine learning engineering, and software engineering.

London Air Quality Tracker
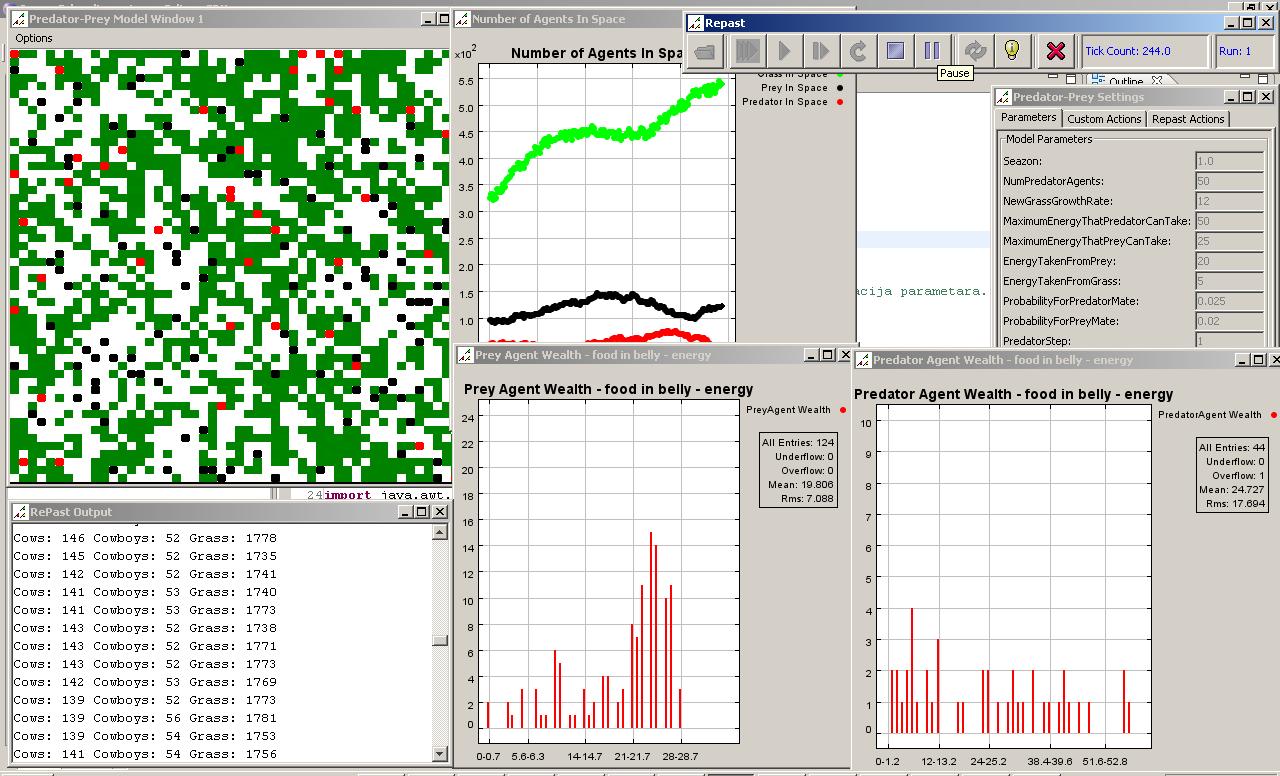
Wild Web - Predator and Prey Simulation
Sunblock Saga

The Orchid Project

Production Management System
for Vinod Rice Mill Pvt Ltd
This project involved developing a full-stack, role-based web application to optimize order processing, internal coordination, and client communication for Vinod Rice Mill Pvt Ltd, a manufacturing business. The system replaced a fragmented manual workflow that relied on multiple applications and direct communication for tracking production, quality control, and shipment status. The project was driven by direct client engagement and a needs analysis that revealed operational inefficiencies stemming from scattered information, delayed updates, and potential for human error. The primary objective was to create a centralized software solution that enhances visibility, accountability, and data consistency, while ensuring ease of adoption within the existing business environment. The core problem addressed was the absence of a unified system for managing order lifecycles across departments with varying responsibilities and access privileges. The system needed to provide role-specific data views while maintaining security, real-time updates, and traceability. The application was built as a role-based web platform using Python, Flask, SQL, HTML, and CSS. Users are authenticated and authorized upon login, then directed to role-specific dashboards displaying relevant functionalities. This access control model ensures data privacy and operational clarity. Administrators possess full system control, including employee management, order oversight, and system configuration. The administrator dashboard facilitates employee account management, detail viewing, employee removal, and order progress monitoring, supporting quality assurance and accountability. Employees are assigned functional roles (e.g., production, finance, shipment), each with a dedicated interface for updating order status within their department. This modular design minimizes cognitive load and prevents unauthorized data modification. Customers interact through a dedicated interface to place orders, view details, track history, and receive real-time updates. This structured communication enhances transparency and customer trust. Orders follow a defined lifecycle, with each update persistently recorded for auditability and analysis. This structured record-keeping enables bottleneck identification, error reduction, and performance evaluation. The system supports order completion, payment tracking, and historical reporting. Technically, the application uses Flask routes for authentication, authorization, and business logic. SQL ensures persistent data storage and consistency. HTML templates and CSS create a clean, role-appropriate interface with shared layout components for maintainability. A key design consideration was phased deployment feasibility, allowing the client to pilot the software, evaluate its effectiveness, and transition gradually, minimizing operational risk and maximizing user acceptance. This approach reflects realistic change-management constraints in small and medium enterprises. The project emphasizes separation of concerns, with clear divisions between authentication, role validation, order management, and UI rendering. Templates are designed for specific user journeys, enhancing clarity and reducing coupling. Development challenges included designing intuitive role-based navigation, preventing unauthorized data access, and ensuring synchronized updates across user views, requiring careful session management, access controls, and database consistency. Key learnings included translating business requirements into software architecture, implementing role-based access control, designing multi-user workflows, and building systems that support real operational processes. The project also enhanced skills in client communication, iterative design, and balancing technical solutions with organizational realities. Future improvements include adding analytics dashboards, automated notifications, finer-grained permissions, and scalability for additional product lines or facilities, potentially extending the system with mobile interfaces or API integrations. Overall, this project demonstrates applied software engineering skills in building secure, role-based, data-driven web applications with real business impact, showcasing the ability to analyze real-world problems, design structured solutions, and implement systems that improve efficiency, accountability, and customer experience.
